Emerging markets present unique opportunities for cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology adoption. In Africa, cryptocurrencies have become a popular alternative to traditional financial systems, especially for those without access to banking services. In addition, blockchain technology is solving traceability problems in the supply chain, managing identities, and solving ownership disputes.
The growing economy and technologically savvy young Vietnamese population have quickly adopted cryptocurrencies as a safe and convenient financial option; meanwhile, the lack of access to banking services and the volatility of the local currency have increased cryptocurrency use in India and Africa.
In each case, digital assets offer a safe and accessible solution to financial problems whilst emerging markets at large present unique opportunities for novel use cases.
Opportunities and use cases in emerging markets
Africa
In Africa, practical use cases are critical to any product success, including Web3 projects. With a relatively low average GDP per capita and financial, social, and environmental infrastructure problems, solutions must either acutely solve a problem or have a clear use case. Some of these use cases include:
- International payments: Web3, in comparison to traditional financial systems, enables faster and cheaper international payments, beneficial in Africa, where many countries have an underdeveloped banking infrastructure.
- Digital identity: Web3 can help address the problem of the lack of legal identities in Africa by enabling the creation of unique and verifiable digital identities that are secure and respect privacy.
- Supply chain traceability: Blockchain technology to trace products along the supply chain, helping to ensure the quality and authenticity of products and reduce fraud in the agricultural and other sectors in Africa.
- Decentralized marketplaces: Web3 can enable the creation of decentralized marketplaces where buyers and sellers can interact directly, without intermediaries. This can be particularly beneficial in farmers’ markets in Africa, where farmers can sell directly to consumers without having to pay exorbitant fees to middlemen.
These Web3 use cases work effectively in Africa because they address specific and pressing problems faced by communities. By leveraging decentralized solutions devoid of centralised control, such platforms are more resilient to regional issues including censorship and manipulation. In this way, Web3 adoption in Africa can help drive financial inclusion and economic development.
To a large extent integration is a main aspect of Web3 adoption in Africa, involving presenting and packaging the technology in a way that is accessible and standardized for the average consumer.
One successful example we can cite here is Fonbnk, which has enabled Africans to obtain cryptocurrency assets by exchanging their airtime credits.
The lack of traditional financial infrastructures in Africa presents opportunities for new technologies such as blockchain, making the integration and gradual advancement essential when 57% of African mobile phones do not have internet access, and only 30% of adults own smartphones in some African countries.
Not only fintech
But the use cases are not only related to the financial market, blockchain technology also has great potential in other non-financial sectors on the African continent. One of the main problems in the region is the lack of reliable and verifiable land ownership records, which leads to disputes and conflicts.
To create transparent and immutable records of who owns what, companies like HouseAfrica and Seso Global use blockchain technology to record land ownership. In addition, blockchain technology can also be used in other sectors, such as healthcare, education, and digital identity, enabling the creation of reliable and verifiable records in these areas. In short, blockchain technology has great potential to solve a wide range of problems in Africa, not just in the financial sector.
India

Although another rapidly growing emerging market, India has a number of unique features that make it something of a special case amongst developing economies. Though the country has shown sustained interest in the crypto sector and an inclination towards new technologies including Web3 and blockchain, it is also true that the lack of clear and successful cryptocurrency regulations has created confusion and hindered the industry growth.
Since the Supreme Court struck down the central bank’s ban on digital currencies in 2020, the Indian government has debated cryptocurrency regulation and legal status without reaching any clear conclusion.
India’s Central Bank, for example, has been particularly wary of cryptocurrencies on the basis of risks, such as money laundering and financial instability. The bank has repeatedly stressed that there have been scams and fraud cases in the cryptocurrency industry in India, which has heightened security concerns. Because of this, banks and financial firms have found it difficult to provide services to cryptocurrency exchanges in this country.
Trading volumes on cryptocurrency exchange platforms in India have declined significantly since the new transaction tax law in July 2022, which provides a 1% tax on all cryptocurrency-related transactions over $126 (INR 10,000). In addition, the Indian government also imposed a 30% tax on all cryptocurrency-related income, leading to a decline in trading activity in the sector.
The cryptocurrencies exodus in India
As a result, many cryptocurrency companies have considered moving to other, friendlier juridsictions such as Singapore or the United Arab Emirates. Dubai is the most obvious beneficiary of this, due to its favorable attitude towards cryptocurrencies and the creation of multiple tax-free zones issuing cryptocurrency licenses.
Sandeep Nailwal, the CEO of Polygon, has indicated on several occasions that he moved his residence to Dubai two years ago because of the same regulatory uncertainty in India that has made it pointless for his company and any other team to expose their protocols to local risks; While he wishes he could live in India and promote the Web 3.0 ecosystem, he has expressed concern about the talent drain that is occurring in the industry. This, he laments, is driving investors, entrepreneurs, and talent away from the country.
Thus we can see how India and the UAE have different perspectives on their approach to Web3 technology and cryptocurrencies; where India has been ambivalent in its approach to cryptocurrencies, while the UAE has taken a more proactive approach, with Dubai recently passing a virtual goods law and establishing an industry watchdog.
In addition, the UAE has also launched a special visa for tech entrepreneurs, allowing them to set up businesses in the country and access resources and funding, attracting many entrepreneurs from around the world and making Dubai an emerging tech hub in the region.
However, it is not all over for India, given that many in the industry hope that its government will try to establish clear and favorable regulations for the sector, considering the country’s potential, positively and drastically changing the landscape in India.
In fact, there are several use cases where Blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and of course, Web3 can make a presence in different sectors, some of which are mentioned below:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The growing worldwide DeFi adoption is also present in India, where users can access decentralized and unmediated financial services such as loans, savings, and interest earnings using cryptocurrencies and blockchain.
- Digital identity: Web3 can also improve the security and privacy of users’ digital identity in India. Storing identity on the blockchain can prevent the exposure of personal data to unauthorized third parties.
- Intellectual property: Web3 can improve intellectual property rights protection by allowing content creators to store and manage their creations on the blockchain, giving them more control over their ownership and distribution.
With a large talent pool in technology and a highly skilled and qualified IT workforce, the digital asset sector has huge potential in India. In addition, the country’s tech adoption rate is high, with a large number of internet users and growing smartphone penetration.
Furthermore, India has been a leader in developing products for international markets. India’s software and IT services industry has been a major exporter of services and has had significant success in providing information technology services globally, meaning that the country has an opportunity to lead in Web3 innovation and provide solutions to global markets.
Finally, there is momentum in the Indian Web3 startup ecosystem. Investment in cryptocurrency and blockchain startups has increased significantly in recent years, and more than 450 Web3 startups are in the country. Some of the most successful include CoinDCX and CoinSwitch.
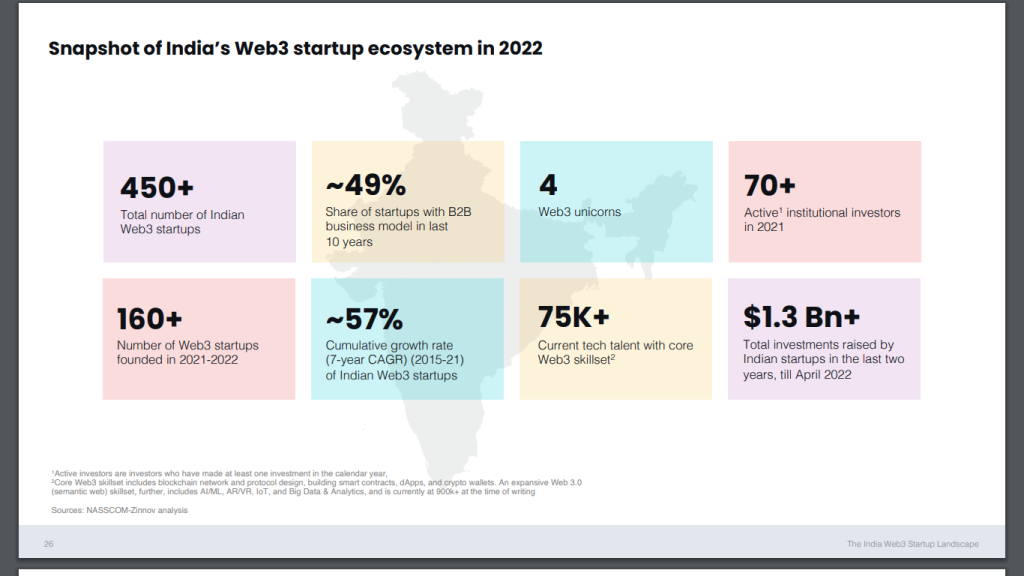
India’s Web3 startup ecosystem by 2022
Source: Nasscom
As seen in the recent NASSCOM study, India has a large talent pool and a high adoption rate of digital technologies, making it a promising market for Web3. Moreover, the gap between supply and talent demand in this area is smaller than in other countries, which means a large pool of skilled professionals is available to work on Web3 projects.
The adoption of cryptocurrencies has also been very significant in India, especially in the last two years, leading to increasing investments in Web3 startups, which have a large market with around 20 million cryptocurrency users. According to the USISPF, this can add $1.1 trillion in economic value to India’s GDP over the next decade. According to the USISPF, this can add $1.1 trillion in economic value to India’s GDP over the next decade.
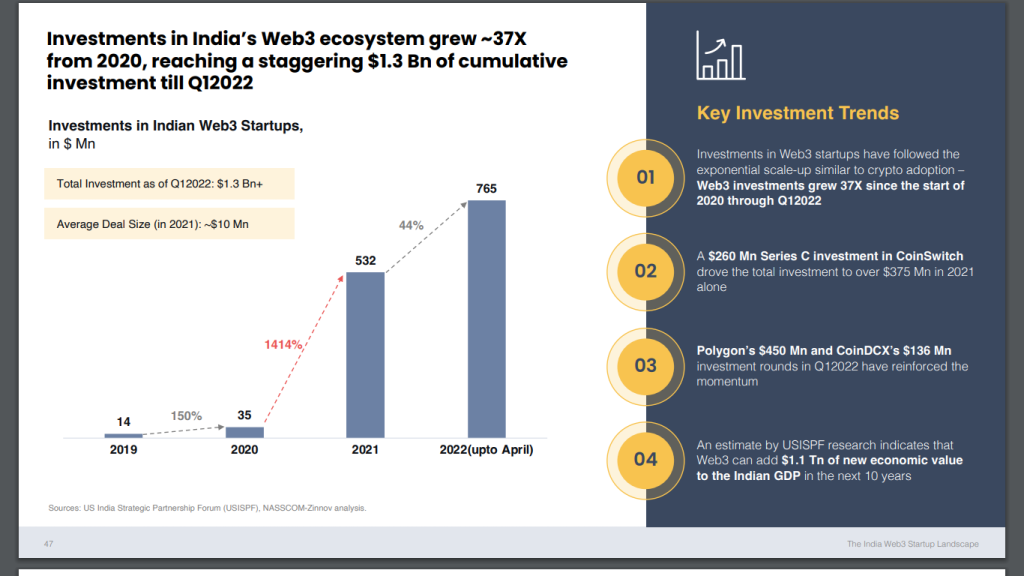
Source: Nasscom
The Indian government has launched various initiatives and programs to foster skills development in emerging and digital technologies, including Web3 and blockchain. On this basis, India has great potential to lead in the adoption and development of emerging technologies, which could significantly impact the country’s economy.
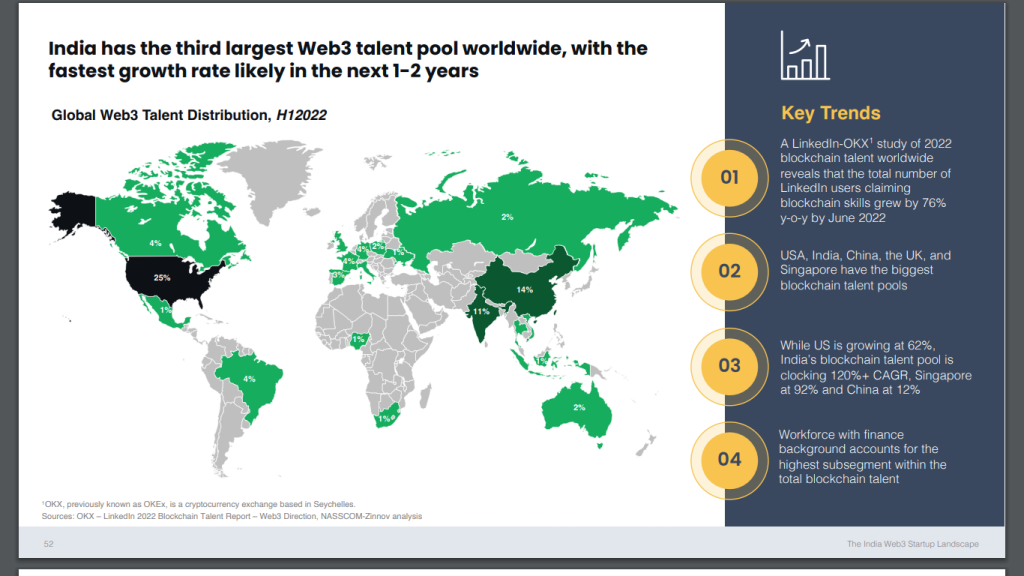
Source: Nasscom
Although India ranks third in the global talent pool for Web3, the study predicts that the growth rate in India’s talent pool will be the fastest in the coming years. Moreover, the country already has a large talent pool in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, which positions it well to lead the development of Web3 and blockchain in the future.
Moreover, we cannot forget that cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can potentially improve Indian fiscal and tax system. Let’s remember that the country has a rather complex tax structure and one of the highest indirect tax rates in the world.
In general, high taxes in India can harm the economy and the population by possibly reducing consumers purchasing power and the competitiveness of businesses. In addition, high taxes can be an incentive for tax evasion and the shadow economy.
Blockchain technology and cryptos could be a solution, given that they can reduce such issues by providing transparent transaction tracking and full traceability. It could also eliminate unnecessary intermediaries, reduce costs and processing times, benefiting small business owners and taxpayers, improving efficiency, and increasing trust and transparency in the tax and fiscal system by allowing all participants to access the same information. However, these technology implementations would require an appropriate strategy and regulations from the government.
The Central Bank digital currency (CBDC) issued by the Central Bank functions as an alternative to traditional fiat currencies. In India, this CBDC could have several benefits, including cost reduction, increased efficiency, financial inclusion, control over the money supply, reduction of the shadow economy, and increased security and transparency. However, its implementation requires proper planning and regulation by the government to ensure its success and benefits for the economy and society.
Vietnam
According to Chainalysis’ Global Cryptocurrency Adoption Index 2022, emerging markets in Asia lead the way in cryptocurrency adoption, with Vietnam in first place and the Philippines in second place; This is even though, in 2018, the State Bank of Vietnam banned cryptocurrencies for use as payment and rolled out fines for companies transacting with them.
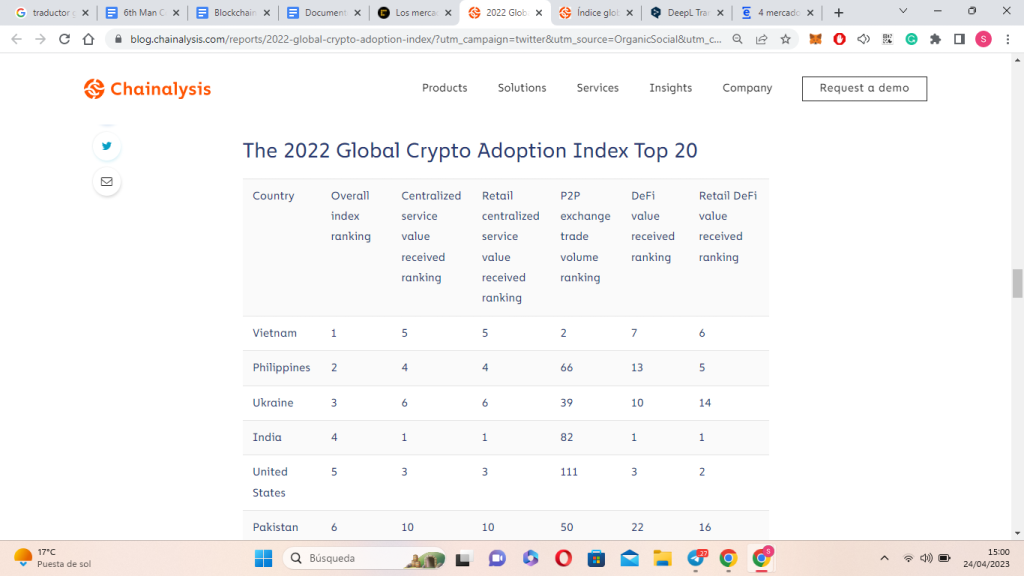
The top five positions in the global cryptocurrency adoption index.
Source: Chainalysis.
Aside from this, the country has no other official regulations regarding blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. However, the approval of the prime minister’s plan to improve the legal framework is a positive sign that the Vietnamese government is recognizing the importance and potential of these technologies and is working to establish a clear and secure regulatory framework.
Such clarity could help foster further growth and adoption of cryptocurrencies and blockchain in Vietnam while helping limit the risks associated with these technologies, namely money laundering and terrorist financing.
Overall, the Vietnamese government’s balanced approach to cryptocurrency and blockchain regulation can help foster a healthy and thriving ecosystem and contribute to Vietnam’s economic and technological development in the future.
The truth is, Vietnam has maintained its position at the top of this ranking for two consecutive years, suggesting that it has established a solid foundation for cryptocurrency use. In addition, the country’s high purchasing power may have influenced its ability to adopt and use centralized crypto, DeFi, and P2P tools.
Meanwhile, the popularity of cryptocurrency-based gaming in Vietnam may also have contributed to the widespread adoption of cryptos in the country. The presence of successful crypto companies in Vietnam, such as Coin98 Finance, Axie Infinity and Kyber Network, may inspire more companies to enter the market and, as a result, further increase adoption in the territory. Chainalysis report also notes that cryptocurrency adoption in Vietnam is high in centralized and decentralized tools, and cryptocurrency-based games, such as P2E and M2E games, are particularly popular.
Vietnamese crypto projects mostly focus on gaming and metaverse, followed by DeFi, NFT, and infrastructure. It is encouraging to see traditional companies integrating blockchain into their operations and the success of Vietnamese crypto projects in raising funds.
However, I believe that whilst the adoption of cryptocurrencies in Vietnam is high, there is a need for solutions to increase the accessibility and usability of cryptocurrencies. So the crypto industry will have to work on creating specific solutions to meet the needs of Vietnamese users and other users in lower-middle and upper-middle-income countries to increase the adoption of cryptocurrencies worldwide.
Blockchain technologies suitable for emerging markets
Having discussed the opportunities and uses cases presented by blockchain technology to emerging markets, we can observe the potential such technology has for future economic growth. For both retail customers and institutional and government players, blockchain’s common purpose of making financial tools available generates a significant value add for regions otherwise lacking in development.
Although there is no single blockchain technology that is suitable for all emerging markets (as each market has its own unique needs and challenges), there are some characteristics that can make blockchain technology more suitable for emerging markets, such as cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility and ease of use, and interoperability.
On this point, we highlight Cardano is a blockchain technology specifically designed to cater to emerging markets. Its focus is on interoperability, sustainability, and financial inclusion through its smart contract platform.
In addition, Cardano uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which consumes less energy than other consensus mechanisms used by other blockchain technologies, such as Bitcoin, making it more accessible and affordable for users in developing countries.
It also focuses on education and training, making it ideal for emerging markets where there is a need for training and skills development in blockchain technology.
In terms of functionality, Cardano has a transaction layer that uses its cryptocurrency, ADA, and a computation layer where smart contracts (dApps) are executed using a language called Plutus, based on the Haskell programming language. Overall, Cardano is an emerging technology that proposes innovative solutions to the limitations of Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Another highlight is that Cardano and Hoskinson’s vision is to use blockchain technology to create a fairer and more people-centered economy, with microfinance as part of that vision.
The collaboration with Pezesha to create a P2P financial system in Africa is an example of how Cardano works to solve real problems and improve access to the economy for all. By enabling people to lend and borrow in a regulated manner, it can facilitate access to finance and foster economic growth in a region that has historically faced difficulties.
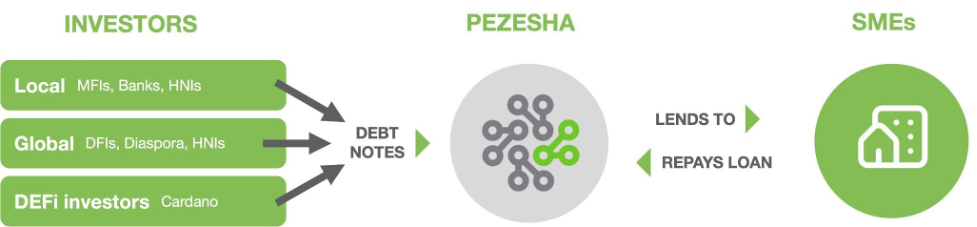
Pezesha is a Kenyan fintech company focused on microfinance, aiming to provide access to affordable loans to small businesses and individuals in Africa.
Cardano’s investment in Pezesha demonstrates the company’s commitment to economic development in Africa while showing its vision of using blockchain technology to solve real problems, such as the lack of access to finance. In short, Cardano has the potential to be a blockchain technology well-suited to emerging markets.
Blockchain technology has the potential to facilitate access to finance in areas where it has traditionally been difficult, especially in Africa, where small businesses are the economic backbone and the absence of access to finance is an obstacle to their growth.
But, in addition to Cardano, I believe there are other blockchain technologies that could be suitable for emerging markets – and although the list may be diverse, I will close this block with my top 3: EOS, Stellar and Aion. Here I explain my interest.
EOS, for example, seems to me an attractive Blockchain technology for emerging markets because of its focus on transaction scalability, with high throughput and low latency, which would help payment applications and microtransactions incredibly.
Block.one has launched several initiatives to encourage the adoption of EOS in emerging markets. For example, in 2019, the company announced a partnership with the online gaming platform Ultra to create an EOS-based gaming platform. In addition, Block.one has launched a $1bn investment fund to support app development on the EOS platform.
However, as with any emerging technology, EOS faces challenges, including competition with other blockchain platforms, such as Ethereum, which has a large developer base and an active community. In addition, security and scalability are focus areas for EOS and its community.
On the other hand, we have Stellar’s technology which allows anyone anywhere in the world to transact coins; This would help developing countries and regions where there is little or no access to financial systems.
But that’s not all, as a plus that I find quite attractive is that the platform also allows the issuance of tokens and the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) that can be used for various purposes, including financial inclusion and humanitarian aid.
Finally, there is Aion, considered very useful for emerging markets, as it provides solutions to the interoperability problems often found in traditional financial systems in these countries. By enabling interoperability between blockchains, Aion could help drive financial inclusion and new financial services in these markets.
However, it is important to evaluate each case individually and consider the specific needs of the market and users before the needs of the market and users before deciding which blockchain technology to use.
Final thoughts
In recent years, blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies have begun to have more presence in emerging markets in Asia, India, and Vietnam. Several projects are underway that use blockchain technology to solve financial inclusion issues and improve efficiency in various industries, such as agriculture and trade.
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies can play a meaningful role in fostering financial inclusion in these emerging markets by enabling people to transact more securely and efficiently without the need for traditional banking infrastructure.
In addition, technologies such as blockchain have the potential to facilitate access to finance in areas where it has traditionally been difficult, especially in Africa, where small businesses are the backbone of the economy and lack of finance is an obstacle to their growth. That’s not to mention how remarkable it is that more than 16.6 million people in Vietnam own cryptocurrencies, where crypto projects focus on gaming, the metaverse, DeFi, and NFT.
India, meanwhile, is well positioned to take advantage of Web3 opportunities, thanks to its large talent pool, the high adoption rate of digital technologies, and growing interest in cryptocurrencies and Web3 startups. However, as we saw throughout the article, it will depend on the regulatory clarity the government establishes for the sector. Otherwise will continue to see the talent and investors drain and the waste of 20 million cryptocurrency users.
While there are still challenges in the widespread adoption of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies in these emerging markets, their use could keep growing in the coming years. In addition, efforts are underway to improve education about these technologies and make them more accessible to individuals.
In summary, the development of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies in the emerging markets of Asia, India, and Vietnam seems to have great potential that I hope can help solve the biggest and most common problem in these regions: financial inclusion and efficiency in various industries. As technology and education on its use continue to evolve, we may see further growth in these emerging markets.